
In today’s fast-paced business environment, effective financial management goes far beyond balancing the books. It plays a critical role in enabling organisations to plan strategically, maintain control, and gain a clear view of their financial position. Yet, as businesses expand and operations become more complex, traditional methods like managing spreadsheets, handling paper records and waiting on manual approvals, struggle to keep up.
This is where modern management accounting steps in. The shift from manual processes to intelligent automation is reshaping how financial teams operate. In this blog, we explore what management accounting entails, why it remains a cornerstone of sound business practice, and how innovative tools are redefining the way organisations manage their finances regardless of size or sector.
What Is Management Accounting?
At its foundation, management accounting refers to the systems and processes used to monitor, analyse, and guide a company’s financial activities. It goes well beyond basic bookkeeping serving as a decision-making tool for budgeting, forecasting, and evaluating performance. By turning raw financial data into structured insights, it empowers businesses to reduce risk, optimise resources, and stay strategically aligned.
To grasp its full scope, it helps to distinguish it from related terms such as financial accounting, cost accounting, and managerial accounting concepts often used interchangeably but with distinct roles and functions.
Management Accounting: Definition and Role
Also known as managerial accounting, management accounting focuses on delivering timely, relevant financial and non-financial information to internal stakeholders such as managers, team leads, and executives. While financial accounting looks backward, reporting historical data to external parties, management accounting looks ahead. It supports daily decision-making and long-term planning through tools like projections, trend analysis, and cost evaluations.
Key activities include budgeting, forecasting, performance reviews, and cost-benefit analysis. The objective isn’t regulatory compliance, it’s business strategy.
Accounting and Management: A Strategic Partnership
The close relationship between accounting and management is central to effective business leadership. When financial data is seamlessly integrated into operations, it becomes a driver of efficiency, agility, and growth. Management depends on accurate, timely accounting information to set targets, monitor performance indicators, and adjust course in response to market shifts.
Distinguishing Financial, Cost, and Management Accounting
A common area of confusion involves the differences among financial, cost, and management accounting. Here’s a concise breakdown:
- Financial accounting focuses on creating standardised reports such as balance sheets and income statements, for external stakeholders like investors, regulators, and tax bodies. It’s historical and governed by formal accounting standards.
- Cost accounting, a branch of management accounting, zeroes in on the costs associated with producing goods or services. It helps businesses refine pricing, control spending, and improve efficiency.
- Management accounting draws from both financial and cost data, but tailors the information for internal use. Its aim is to support strategic decision-making, not regulatory reporting.
Together, these disciplines form a comprehensive financial framework that supports sound business operations and smarter decision-making.
Functions and Objectives of Management Accounting
Management accounting plays a pivotal role in both the daily operations and long-term strategy of an organisation. Its purpose extends far beyond recording numbers. It focuses on interpreting financial data to uncover patterns, assess performance, and guide better business decisions.
Let’s examine the key functions and objectives that define management accounting and why they matter.
Core Functions of Management Accounting
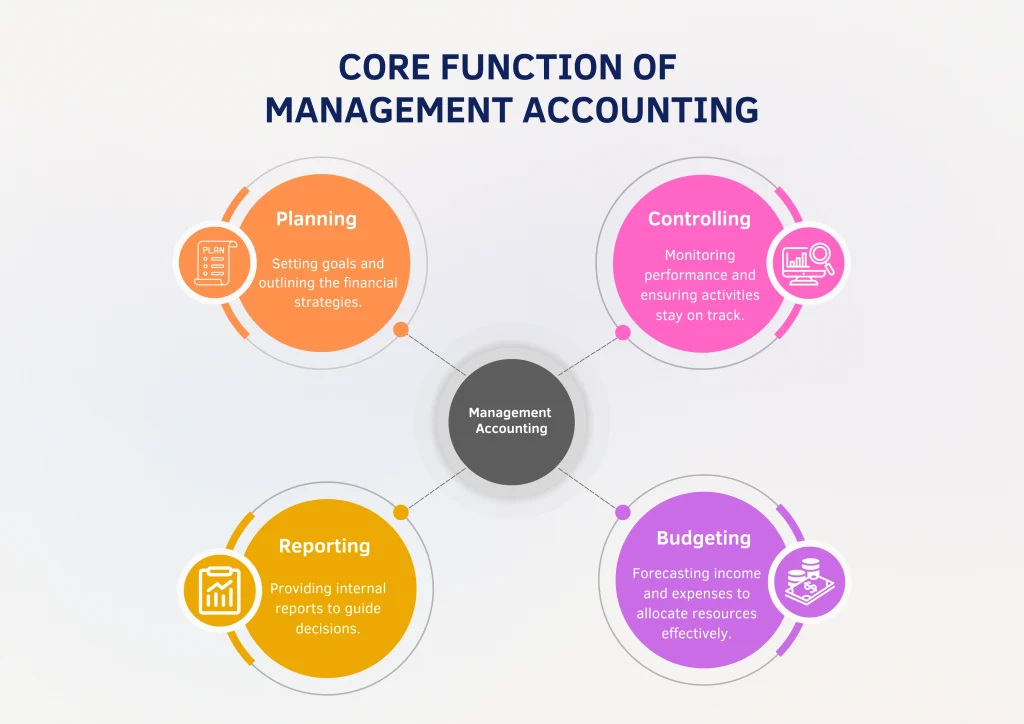
At its core, management accounting supports internal decision-making and drives financial efficiency. Its primary functions include:
- Planning: Assists in setting financial objectives and outlining strategies to achieve them. This includes forecasting revenues, preparing budgets, and aligning financial plans with broader organisational goals.
- Controlling: Tracks actual performance against budgets and plans. When deviations occur, management accounting helps identify the causes and supports corrective action.
- Reporting: Delivers tailored financial and operational reports to internal stakeholders. These reports are often more detailed and adaptable than standard financial statements, offering insight into key business metrics.
- Budgeting: Develops structured financial plans that guide departmental or project-level spending. Budgets support resource allocation, cost control, and the measurement of success.
These functions equip managers with the financial intelligence needed to make timely, informed decisions that align with strategic priorities. To control costs effectively, organisations must not only track spending but also understand the difference between purchasing and procurement, as each plays a distinct role in managing supplier relationships and financial outcomes.
Key Objectives of Management Accounting
The objectives of management accounting are centred on enhancing organisational performance and decision-making through accurate and relevant financial oversight. These objectives include:
- Cost Control: Identifies and reduces unnecessary expenses by highlighting inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Decision Support: Provides dependable data and analysis to inform strategic choices—whether in pricing, investment, operations, or resource allocation.
- Performance Evaluation: Measures the effectiveness of business units, teams, or projects by comparing actual outcomes against established targets.
These objectives ensure that financial decisions support the broader vision of the organisation, fostering both operational efficiency and sustainable growth.
The Importance of Management Accounting
In a fast-moving and data-driven business landscape, the ability to turn complex financial data into actionable insight offers a distinct advantage. It does more than explain what has happened. It equips organisations to plan ahead and adapt with confidence.
From sharper forecasting to disciplined budgeting and real-time cost management, management accounting enables businesses to navigate uncertainty and seize new opportunities. It’s a vital function for any organisation striving to remain competitive and resilient.
Key Features of Management Accounting
What makes management accounting so effective? Its features are designed to meet the evolving needs of modern business:
- A forward-looking approach, focused on future performance rather than past results
- Customised internal reporting that adapts to managerial needs
- Integration of both financial and non-financial data
- Emphasis on strategic planning and decision-making
- Flexibility in reporting format and scope to suit specific business contexts
These characteristics make it, a dynamic and indispensable part of today’s business toolkit.
Decision-Making in Management Accounting
In any organisation, the quality of decisions made has a direct impact on profitability, resilience, and long-term growth. This is where management accounting becomes indispensable—turning raw financial data into strategic insights that guide choices across functions and levels.
What Is Decision-Making in Management Accounting?
Decision-making in management accounting involves using both financial and operational data to evaluate options and determine the most effective course of action. Whether assessing a new investment, adjusting pricing strategies, or reallocating resources, it provides the analytical framework that supports confident, evidence-based decisions.
Rather than simply tracking figures, it involves interpreting trends, modelling scenarios, and forecasting outcomes—ensuring decisions serve the organisation’s wider goals.
Management accounting acts as both a strategic compass and a performance dashboard for decision-makers. It enables leaders to:
- Evaluate alternatives using cost, revenue, and performance data
- Understand the financial implications of strategic initiatives
- Align choices with organisational objectives and financial health
- Monitor progress and adjust plans dynamically
By delivering timely, relevant, and forward-looking information, it reduces uncertainty and supports agile, informed responses to business challenges.
Overcoming Traditional Challenges in Management Accounting
Before the rise of digital platforms, management accounting was largely driven by manual, paper-based processes. While once adequate, these outdated methods now present critical challenges particularly as businesses face increasing complexity and demand for speed.
One of the most pressing issues is the time lag inherent in manual workflows. Paper forms, spreadsheet-based tracking, and physical approvals introduce delays in data entry, reporting, and decision-making. These bottlenecks can slow entire operations, preventing managers from responding swiftly to evolving business needs.
Accuracy is another concern. Manual data entry is inherently error-prone; whether through typos, formula mistakes, or misinterpretation and these errors often remain undetected until they affect budgets, forecasts, or compliance efforts.
Manual systems also create limited visibility. Without a centralised source of financial truth, key data is scattered across files, folders, and inboxes, making it difficult to obtain a real-time or historical view of financial performance.
Additionally, disconnected systems often lead to siloed operations. When departments manage costing, budgeting, and expenses independently, inefficiencies emerge—ranging from duplicated work to miss updates—making it harder to coordinate efforts across the organisation.
In a data-driven world, these challenges increase the risk of poor decisions and missed opportunities, highlighting the need for a smarter, more connected solution.
The Shift to Smart Automation in Accounting
To improve speed, accuracy, and visibility, many organisations are transitioning from manual systems to automated accounting solutions. This shift marks a fundamental transformation in how financial data is captured, processed, and used.
Accounting automation involves using digital tools to streamline routine financial tasks, from real-time expense approvals to integrated reporting. Instead of relying on spreadsheets and physical documents, teams operate within centralised platforms that eliminate duplication and increase control.
Automation also brings order and structure to processes like approvals and expense tracking; often closely tied to workflows such as what is purchase order management, where timely and accurate data is essential.
Benefits of Accounting Automation
Implementing automation in management accounting offers clear advantages:
- Speed: Tasks such as approvals, reporting, and reconciliations happen faster, without manual delays.
- Transparency: Real-time data access allows teams to monitor performance, identify trends, and act proactively.
- Error Reduction: Automated inputs reduce the risk of human error, ensuring more reliable data for decision-making.
- Control and Consistency: Defined workflows and rules help standardise processes and strengthen compliance.
How CMS Desk Supports This Transformation
CMS Desk’s suite of modular applications is designed to support the shift toward smarter, more efficient financial management—regardless of your industry or operational scale.
- The CMS Costing App enables real-time tracking of project or departmental expenses, equipping teams with instant access to cost data and performance metrics for more informed, agile decisions.
- The CMS Voucher App simplifies on-site payments and approvals, providing a seamless experience for managing expenses across multiple locations. From voucher creation to payment tracking and reporting, everything operates within one connected digital environment—reducing paperwork and improving oversight.
Together, these tools empower businesses to move beyond the limitations of manual accounting, adopting a more intelligent, streamlined, and strategic approach to financial management.

Conclusion: Smarter Accounting for a Smarter Business
In today’s fast-moving and data-centric world, traditional, manual accounting processes can no longer support the level of insight and agility businesses need. Management accounting has evolved into a strategic function—offering the financial clarity, context, and control required to navigate uncertainty, make confident decisions, and drive sustained success.
By embracing automation, organisations not only enhance accuracy and reduce costly errors but also free up time for high-value activities like forecasting, planning, and innovation. Whether tackling operational challenges or shaping long-term strategy, modern management accounting empowers teams to unlock value at every level.
If your organisation is ready to move beyond outdated methods, CMS Desk offers a forward-looking solution. With our Costing and Voucher apps, you gain real-time visibility, streamlined processes, and the strategic control needed to thrive in a competitive landscape.
Take the first step toward smarter management accounting—discover CMS Desk today.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is accounting financial management?
Accounting financial management refers to the integration of financial accounting principles with broader financial planning and decision-making processes. It involves managing a company’s financial resources — including budgeting, forecasting, investment analysis, and risk management — while ensuring accurate reporting and compliance. This combined approach helps businesses make informed, strategic financial decisions based on reliable data.
2. What does a management accountant do?
A management accountant provides financial insights and analysis to help organisations plan, monitor, and control their operations. Unlike financial accountants, who prepare reports for external stakeholders, management accountants focus on internal decision-making. Their responsibilities typically include budgeting, cost analysis, forecasting, performance evaluation, and supporting strategic initiatives.
3. What is earnings management in accounting?
Earnings management is the practice of using accounting techniques to influence reported financial results. While it can be used to smooth out fluctuations and present a stable performance, it can also be problematic if used to mislead stakeholders. Ethical management accounting relies on transparency and accuracy, ensuring earnings reflect the true financial health of the organisation.
4. What is break-even analysis in management accounting?
Break-even analysis is a tool used in management accounting to determine the point at which total revenue equals total costs — meaning the business is neither making a profit nor incurring a loss. This analysis helps decision-makers understand how changes in cost, price, or volume impact profitability and is often used in pricing strategy, investment planning, and cost control.
5. What is environmental management accounting?
Environmental management accounting (EMA) combines traditional accounting with environmental considerations. It tracks the costs and benefits of a company’s environmental practices — such as energy use, waste management, and resource efficiency — to support sustainable decision-making. EMA helps businesses not only reduce environmental impact but also uncover opportunities for cost savings and innovation.
Any questions? Get in Touch